Vue enables you to define more than one props against a component. Defining props and passing around values are one of the ways of getting components to react to values passed to them (think arguments), or talk to each other :).
See which component communication is effective and how props compare to Vuex
Defining prop in a component is simple enough -
<!-- Target.vue -->
<template>
{{ tinyInput }}
<!-- display the prop -->
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
tinyInput: {
type: String,
required: false
}
}
};
</script>
You can now call this component from another component/view like so -
<!-- Source.vue -->
<template>
<Target tinyInput="I am Tiny" />
</template>
<script>
export default {
components: { Target: () => import("./Target") }
// lazy load!
};
</script>
You can also use props when calling component from a router.
Required prop
You can make a prop required by specifying - you guessed it - required to true.
<!-- Target.vue -->
<template>
{{ tinyInput }} {{ tinierIn }}
<!-- display the prop -->
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
tinyInput: {
type: String,
required: true
}
}
};
</script>
Receiving props without definition
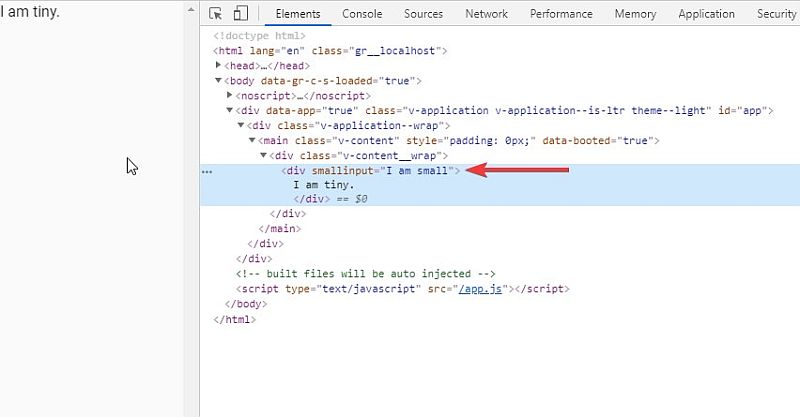
While defining props is the best practice, you can get away without doing so. But of course, you cannot use it within your component directly. The passed value is included in the root element of the component. This is known as “non prop attributes”.
Source -
<template>
<Target tinyInput="I am tiny." smallInput="I am small" />
</template>
Target -
<template>
<div>
{{ tinyInput }}
<!-- display the prop -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
tinyInput: {
type: String,
required: false
}
}
};
</script>
Prop Types
Type of a prop can be one of the following -
- String
- Number
- Boolean
- Array
- Object
- Date
- Function
- Symbol
Reference: Vue Docs
Expect a warning in console if the source does not pass prop of the expected type. So, handle your errors within your component - improper errors can destroy humanity as we know it.
Use default values with props
Specify default value in the prop definition like so-
<template>
<div>
{{ tinyInput }}
<!-- display the prop -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
tinyInput: {
type: String,
default: "hello world",
required: false
}
}
};
</script>
Pass dynamic value in props
You will not often find yourself sending static text in prop like defined in the above examples. You just bind values to send a dynamic prop value.
Source -
<template>
<v-app>
<v-content>
<Target :tinyInput="tinyVar" />
</v-content>
</v-app>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data: () => ({
tinyVar: "I am tiny var"
})
};
</script>